A powered simple walking model explains the decline in propulsive force and hip flexion torque compensation in human gait
$ 24.99 · 5 (322) · In stock


The mechanisms and mechanical energy of human gait initiation from the lower-limb joint level perspective
Research articles Scientific Reports

Joints kinematics of the simulated bipedal robot.
Research articles Scientific Reports

Two gait models used in this study. (a) Simplest walking model with a

Locomotion Laboratory
Research articles Scientific Reports
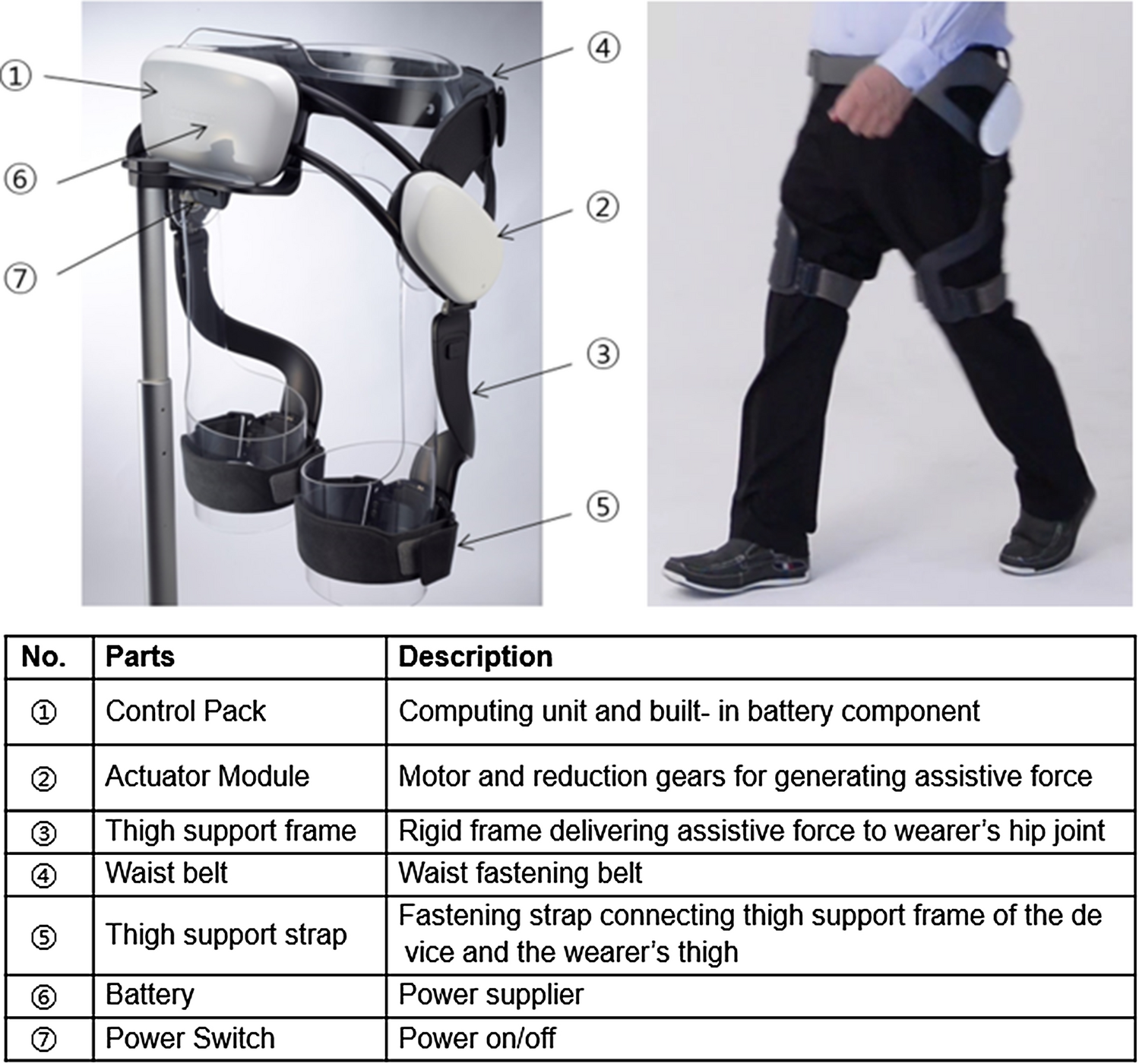
Exercise with a wearable hip-assist robot improved physical function and walking efficiency in older adults

Investigation of the relationship between steps required to stop and propulsive force using simple walking models - ScienceDirect

Motion Trajectory Optimization of an Assistive Device During

Modeling the Effects of Linear and Torsional Spring Based Passive Assistance on Human Gait

A powered simple walking model explains the decline in propulsive force and hip flexion torque compensation in human gait

Snapshots of the simulated bipedal robot. (A) 0.5 m/s (B) 0.8 m/s (C)

Investigation of the relationship between steps required to stop and propulsive force using simple walking models - ScienceDirect

a) Relationship between the natural frequency