SOLVED: For a gas at a given temperature, the compression factor is described by the empirical equation: z = 1 - 8.50 × 10^(-3)P/P° + 3.50 × 10^(-5)(P/P°)^2 where P° = 1
$ 16.00 · 4.6 (260) · In stock
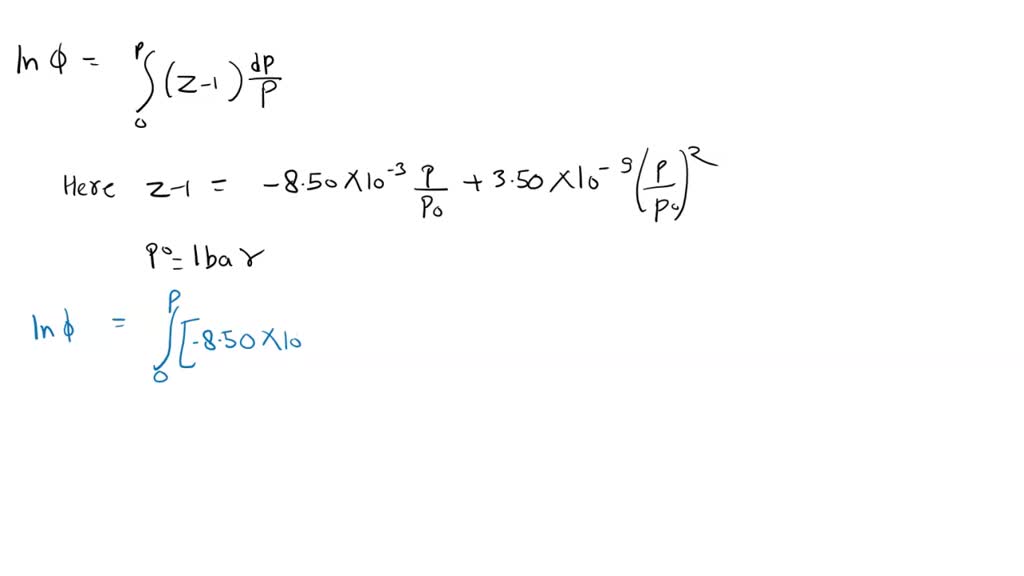
VIDEO ANSWER: Hello students: let's look at the question: l n, that integrate integration and 0 z minus 1 bracket, close d p by p here. Minus 1 is equal to minus 8.50 into 10 to the power minus 3 p by p, not plus 3.50 into 10. To the power minus 9. P
Numerade is a venture-backed, high-growth education technology startup based in Pasadena. We are singularly focused on creating exceptional video and interactive content experiences for education making the knowledge and skills of world class educators widely accessible and affordable to student audiences of all backgrounds. Our mission is to close the educational opportunity gap by unlocking and democratizing access to extraordinary educators and the content they have to offer.

Calculate the compressibility factor for a gas, if 1 mole of it occupy 0.821 litre at 300 K and 50 atm.A. 1.33B. 1.67С. 0.67D. 1

EXAMPLE PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS McGraw-Hill Education - Access Engineering
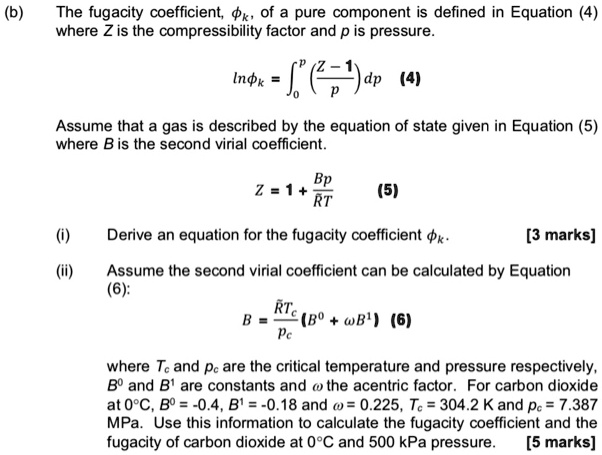
SOLVED: The fugacity coefficient of a pure component is defined in Equation 4, where Z is the compressibility factor and p is pressure. nk = 4 Assume that a gas is described

Thermodynamics - 3-7 Ideal Gas Equation with compressibility factor
Metals, Free Full-Text

SOLVED: 1. Find the temperature of n-pentane gas at 2,400 kPa if its molar density is 0.650 kmol/m³. Use the Redlich-Kwong (RK) equation and the following form of the cubic equation of

EXAMPLE PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS McGraw-Hill Education - Access Engineering
Computation of The Compression Factor An, PDF, Gases
Compressibility Factor Z

NCERT Chemistry 1 class 11 by junaid fardeen - Issuu
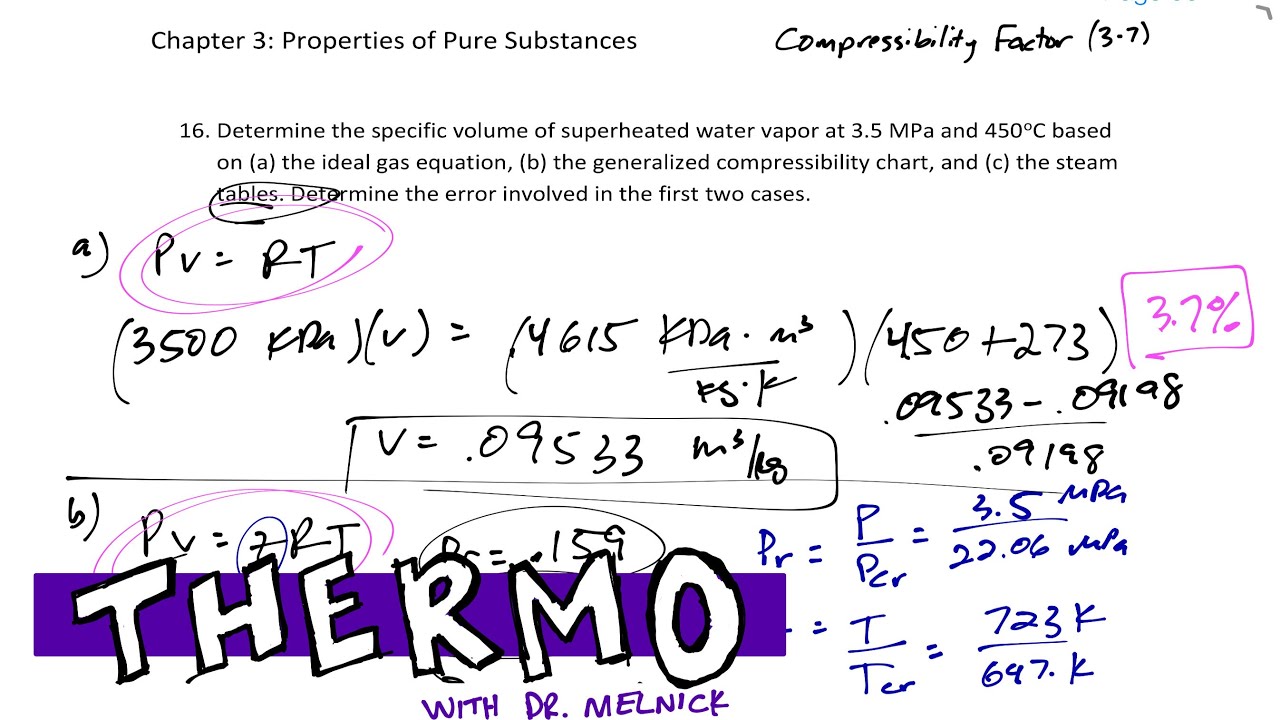
Thermodynamics - 3-7 Ideal Gas Equation with compressibility factor example 2
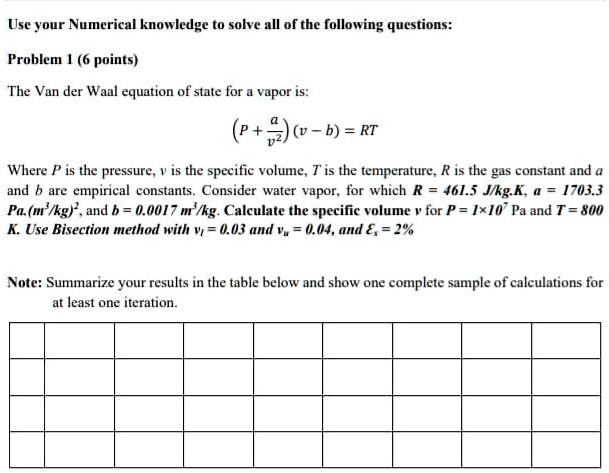
SOLVED: Use our numerical knowledge to solve all of the following questions: Problem (6 points) The Van der Waals equation of state for vapor is: (P + a/v^2)(v - b) = RT

