Downregulation of microRNA-34 induces cell proliferation and
$ 27.00 · 4.8 (722) · In stock
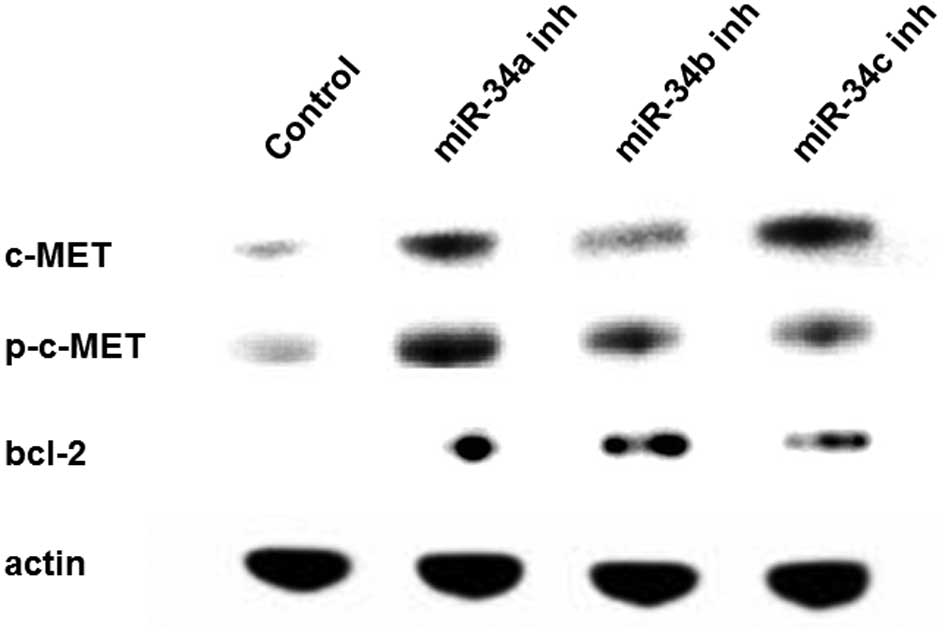
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is an aggressive tumor with a dismal prognosis, and the molecular alterations involved in this disease remain unknown. We previously reported that microRNA-34s (miR-34s) are methylated and downregulated in MM and may play an important role in the carcinogenesis of MM. In this study, we downregulated miR-34s in human mesothelial cells to investigate the cellular effect of miR-34 knockdown. For the cell study, we used LP-9, a human mesothelial cell line, and three human primary-cultured mesothelial cell lines. RNA-based miR-34a, -34b and -34c inhibitors were transfected into these cells, and their effects on proliferation and invasion were evaluated. A scramble RNA oligonucleotide was used as a control. The protein expression status was estimated using western blotting. After miR-34 inhibitor transfection, miR-34a, -34b and -34c were downregulated in all the examined mesothelial cell lines. miR-34 inhibitor transfection significantly increased cell proliferation in all of the mesothelial cell lines, compared with the scramble control. The invasive ability also increased in the miR-34 inhibitor transfectants, compared with the scramble control, in the LP-9 cell line. Western blotting confirmed the upregulation of c-MET, phospho-c-MET, and bcl-2 proteins in LP-9 cells after miR-34 inhibitor transfection. In conclusion, our study showed that the downregulation of miR-34s induced an oncogenic phenotype in non-malignant mesothelial cells. The present study, together with the results of our previous report, strongly suggest that miR-34s play an important role in the early carcinogenic process involved in the transformation of human mesothelial cells to MM.

Meta-analysis of miR-34 target mRNAs using an integrative online application - Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal
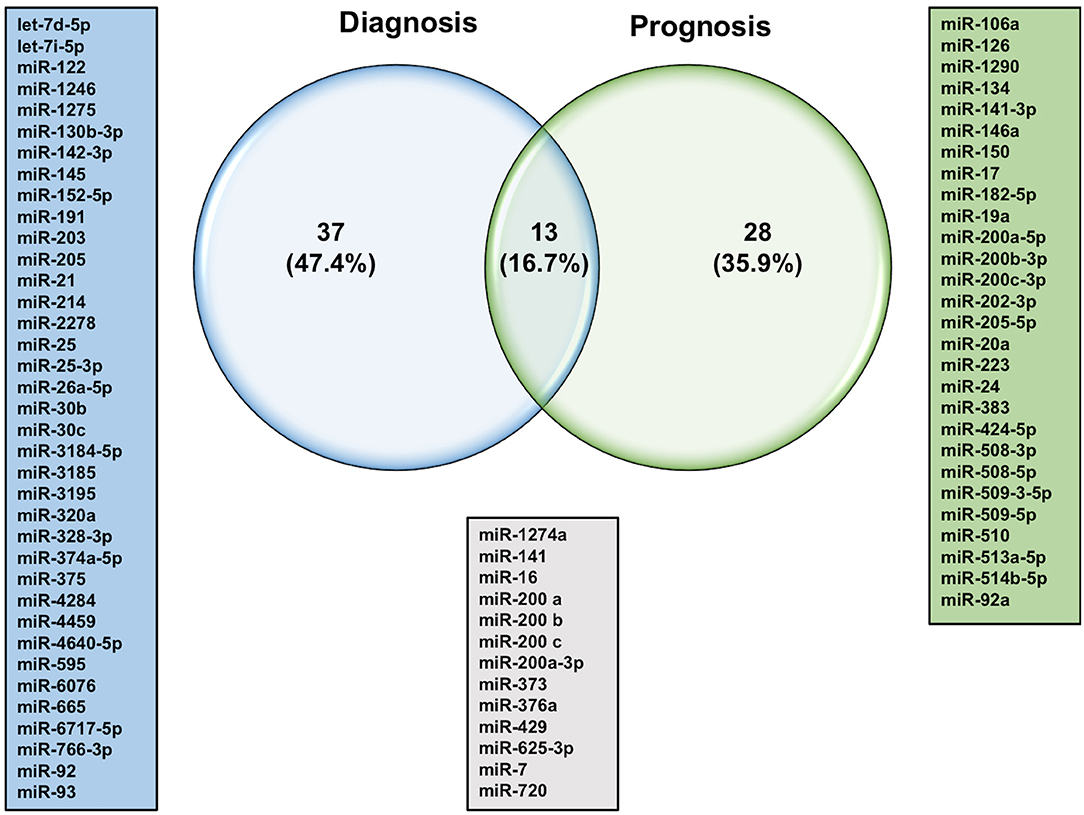
Frontiers Roles of microRNAs in Ovarian Cancer Tumorigenesis: Two Decades Later, What Have We Learned?

PDF) Manipulating microRNAs for the Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Past, Present and Future

Relations between approved platinum drugs and non-coding RNAs in mesothelioma - ScienceDirect
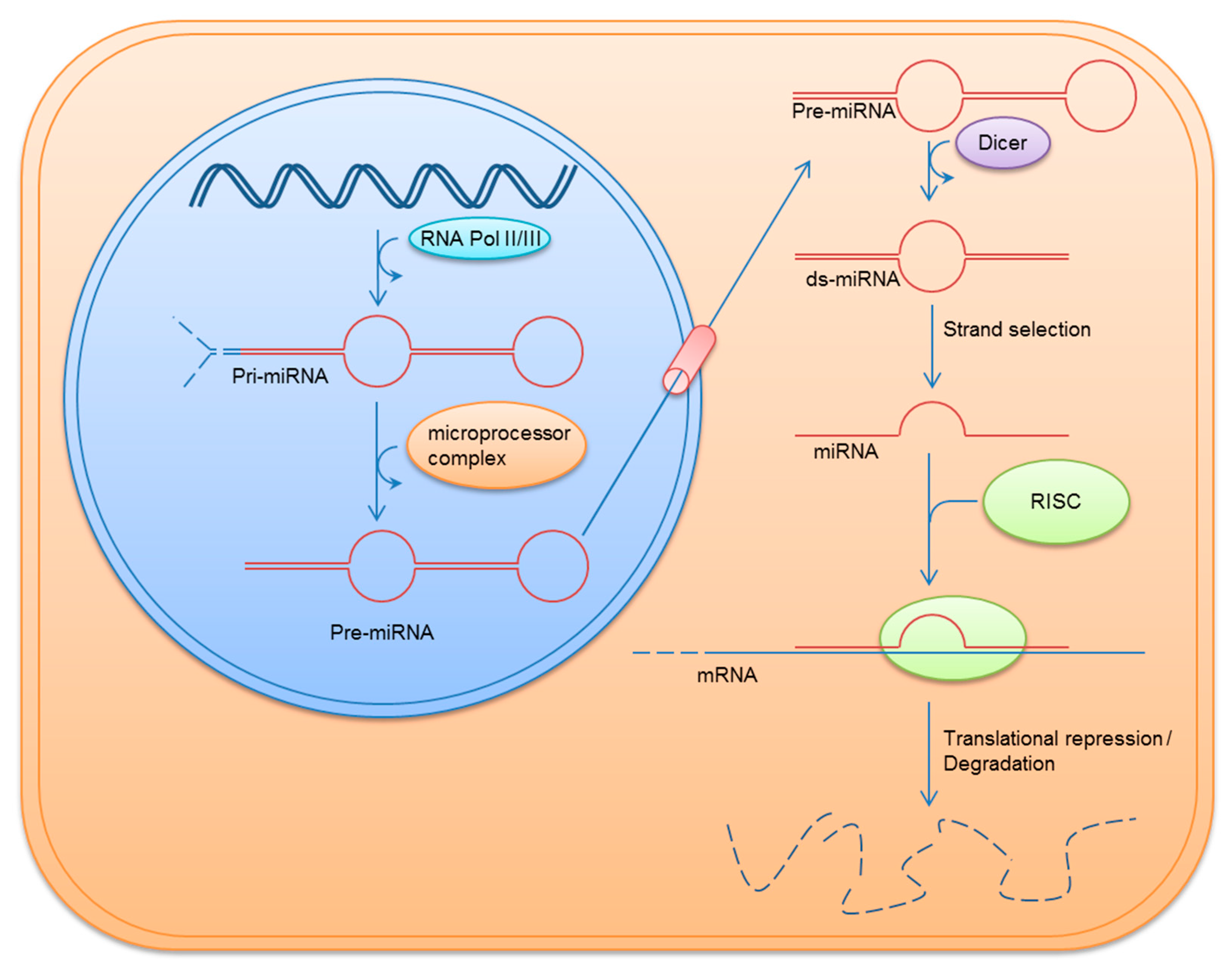
IJMS, Free Full-Text
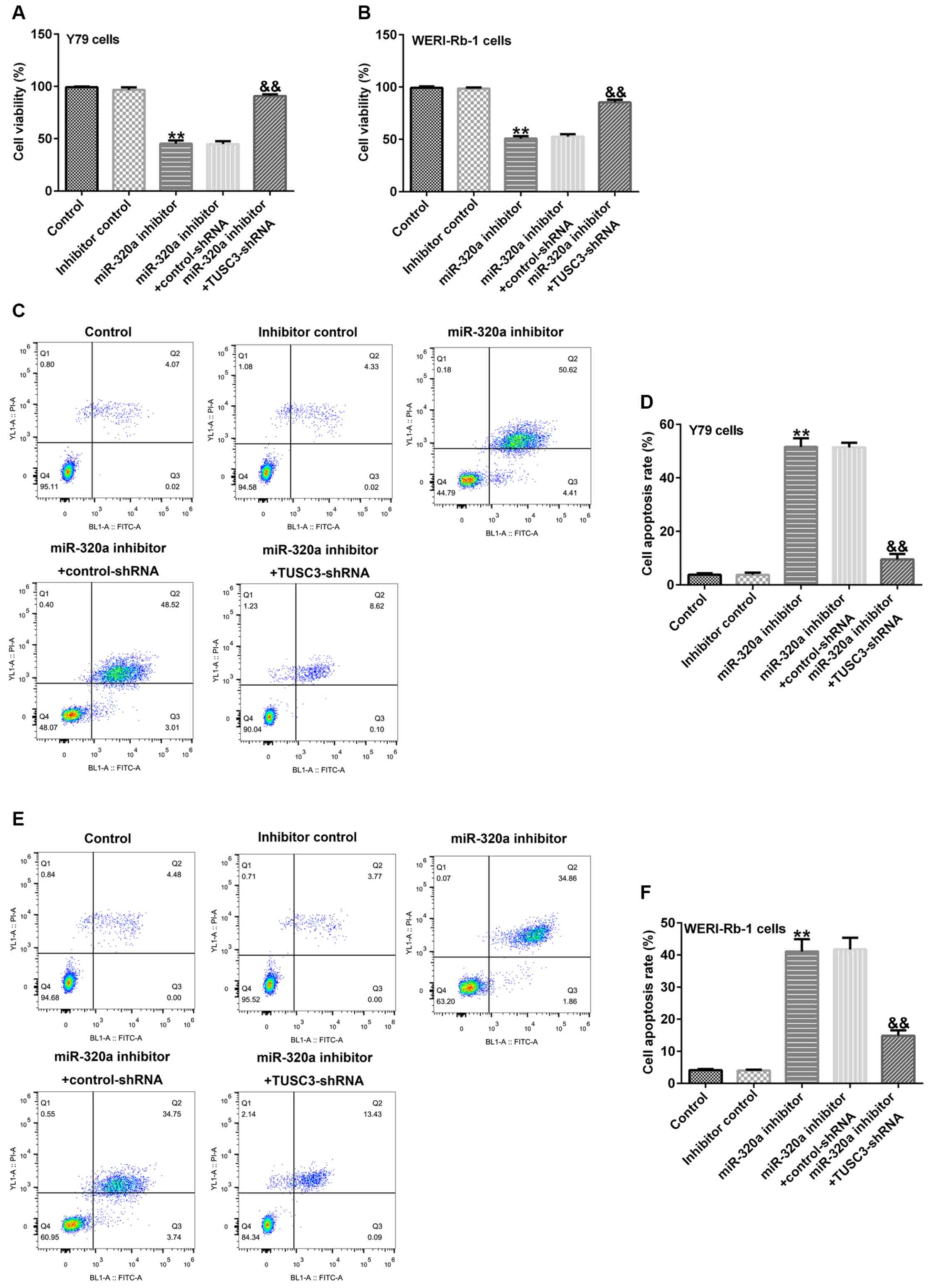
Downregulation of microRNA‑320a inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells via targeting TUSC3

Deciphering signaling pathway interplay via miRNAs in malignant pleural mesothelioma - ScienceDirect

A comparison between the effects of over-expression of miRNA-16 and miRNA-34a on cell cycle progression of mesothelioma cell lines and on their cisplatin sensitivity - ScienceDirect

MicroRNA-34 family: a potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in cancer, Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research

PDF) Mir-34: A New Weapon Against Cancer?

Mir-34: A New Weapon Against Cancer? - ScienceDirect

MicroRNAs and the cell cycle - ScienceDirect

IJERPH, Free Full-Text

PDF) Promising therapeutic potential of tumor suppressor microRNAs for malignant pleural mesothelioma
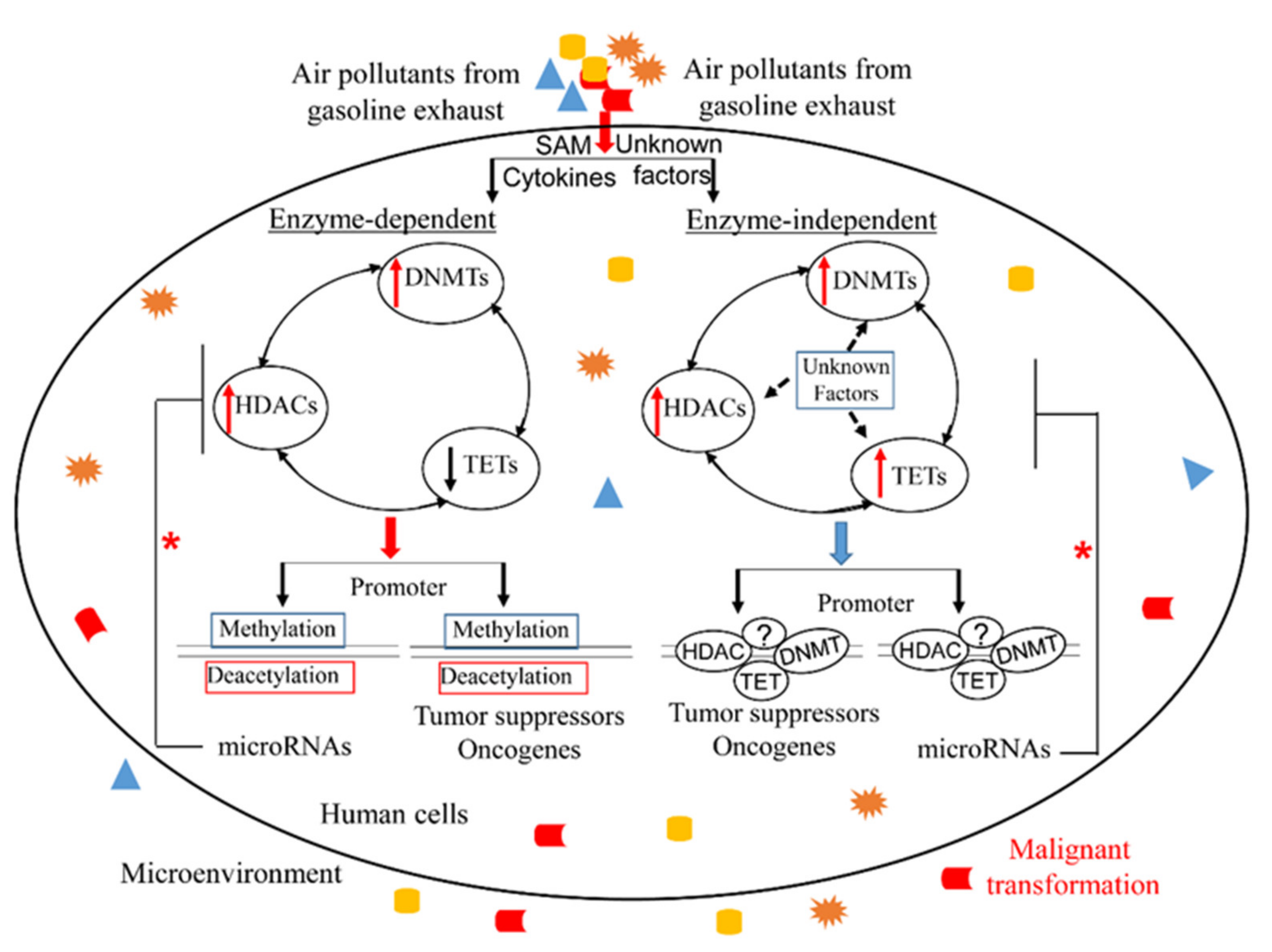
IJERPH, Free Full-Text