Figure 1 from When fat becomes an ally of the enemy: adipose tissue as collaborator in human breast cancer
$ 6.50 · 4.5 (308) · In stock

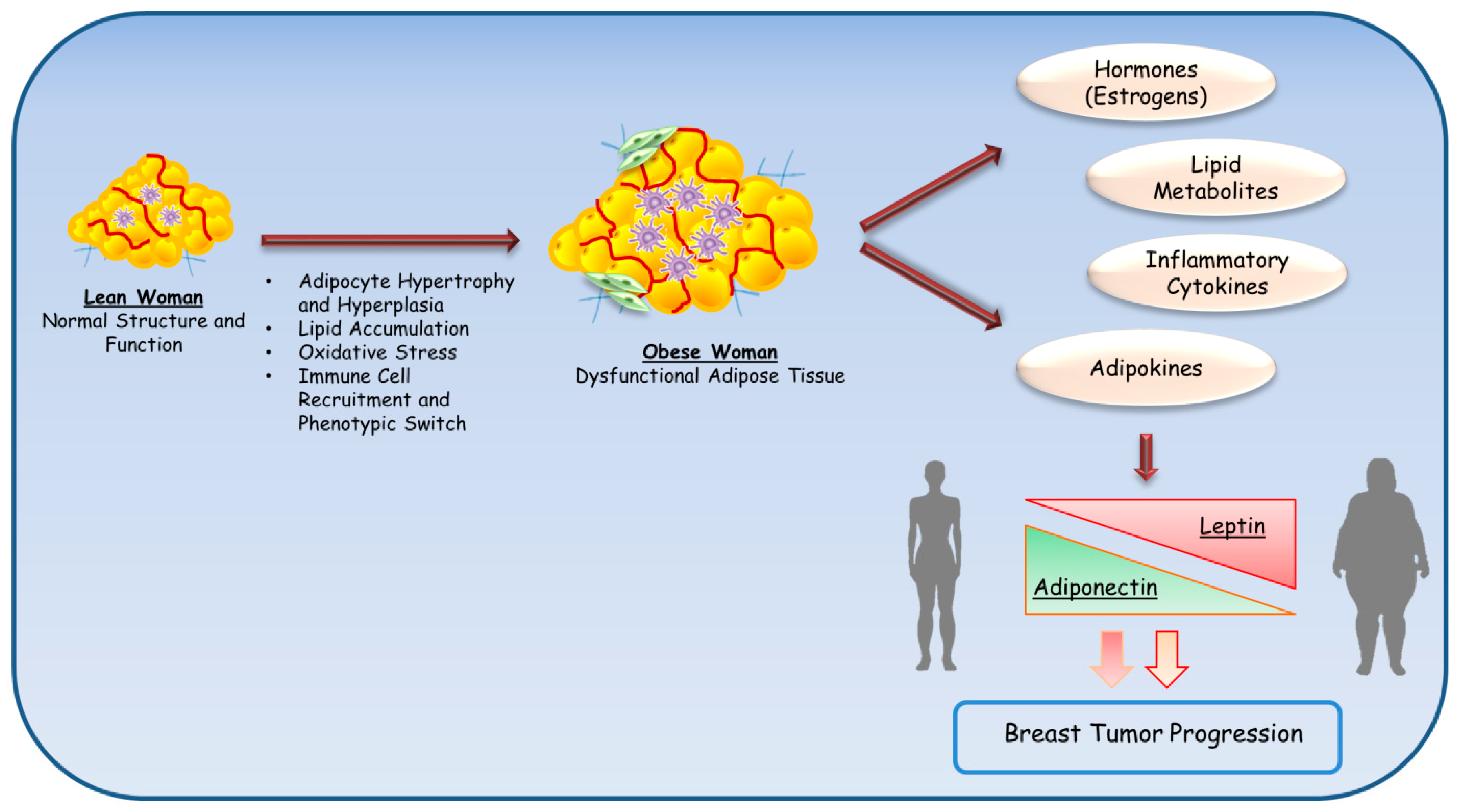
Figure 1: Normal adipose tissue has the capacity to stimulate human breast cancer tumorigenesis and progression. The production of steroid hormones, adipokines, triglycerides, and free fatty acids are the major functions of normal adipose tissue of which, several molecules have the potential to influence different aspects of breast cancer. - "When fat becomes an ally of the enemy: adipose tissue as collaborator in human breast cancer"

Adipocyte lipolysis links obesity to breast cancer growth: adipocyte-derived fatty acids drive breast cancer cell proliferation and migration. - Abstract - Europe PMC
The role of three-dimensional in vitro models in modelling the inflammatory microenvironment associated with obesity in breast cancer, Breast Cancer Research

Figure 1 from When fat becomes an ally of the enemy: adipose tissue as collaborator in human breast cancer
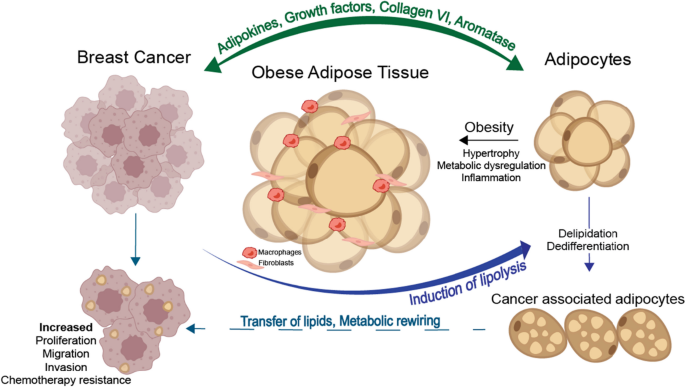
Frontiers Obese Adipose Tissue as a Driver of Breast Cancer Growth and Development: Update and Emerging Evidence
Is fat blob in stomach dangerous? - Quora

Pathways Winter 2016/2017 (Volume 6, Issue 1) by Canadian Lymphedema Framework - Issuu

Baseline Characteristics of Diabetic Women with Breast Cancer, by

JCI - Breast milk alkylglycerols sustain beige adipocytes through adipose tissue macrophages

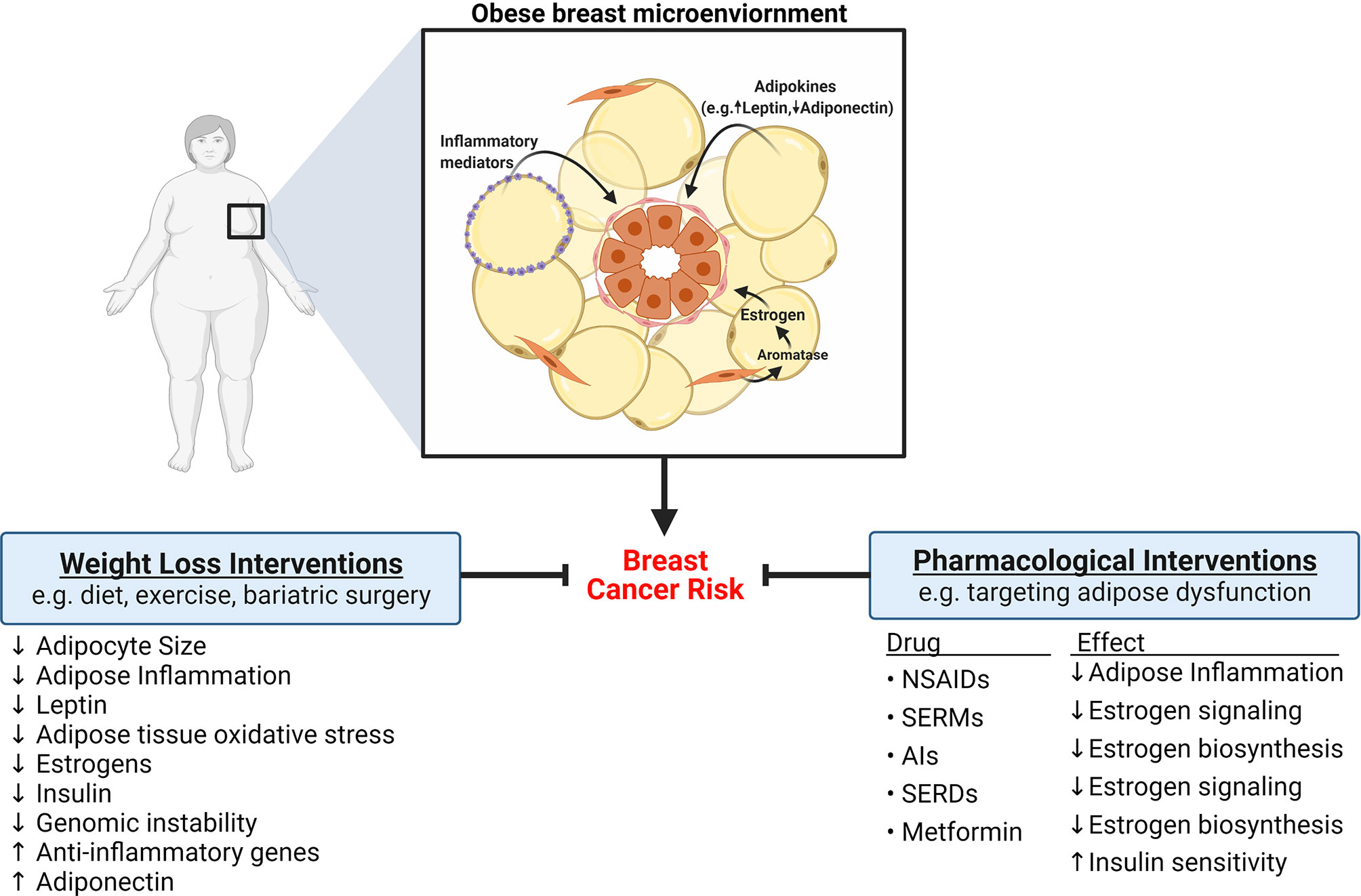
Adipose tissue-to-breast cancer crosstalk: Comprehensive insights - ScienceDirect
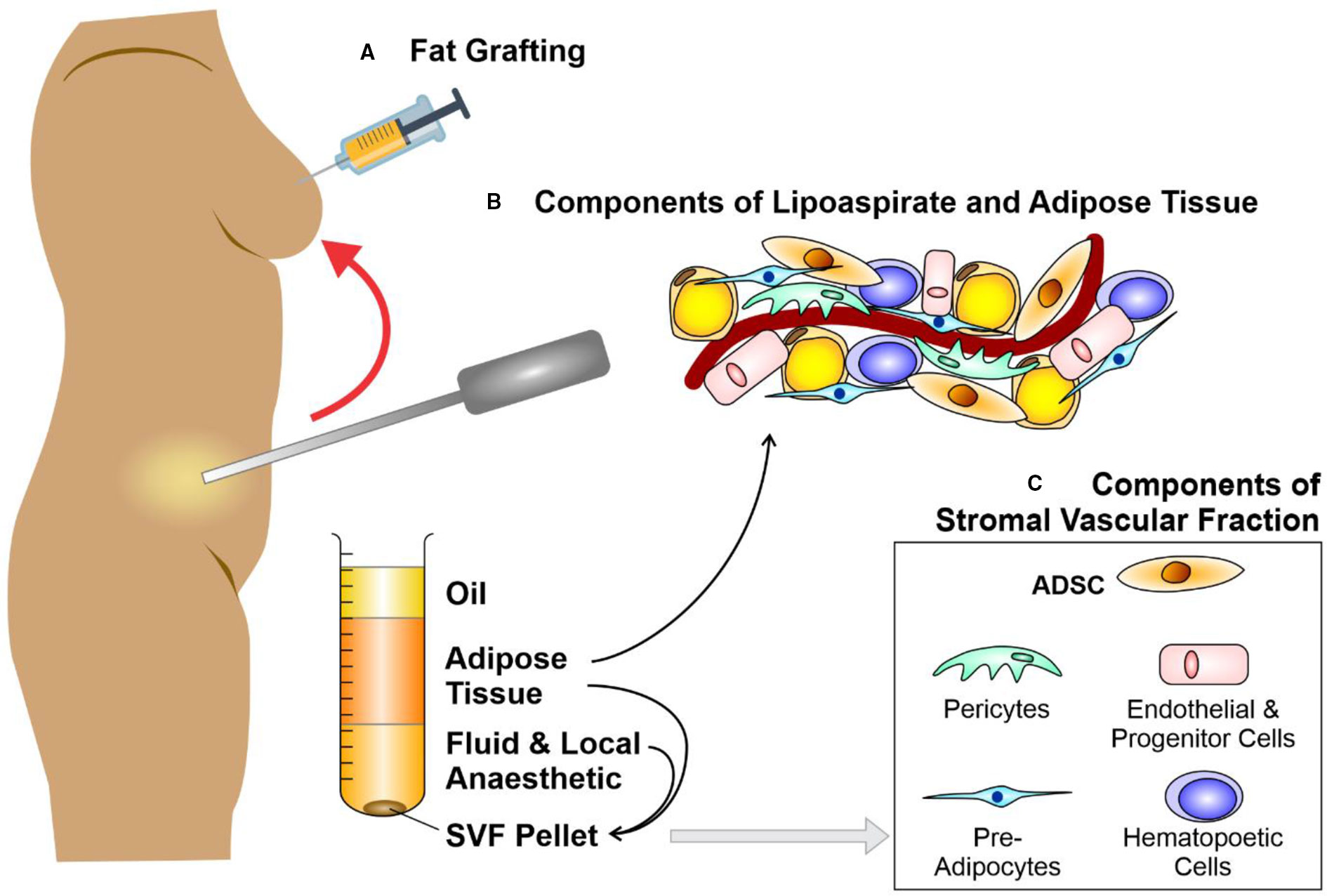
Frontiers Fat Therapeutics: The Clinical Capacity of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Exosomes for Human Disease and Tissue Regeneration

Tumor suppressor BRCA1 inhibits a breast cancer-associated promoter of the aromatase gene (CYP19) in human adipose stromal cells
Cancers, Free Full-Text