When you are given two sides of a right triangle, how do you find the third side?
$ 23.99 · 5 (600) · In stock
Using the Pythagorean theorem which applies exclusively to right-angled (or right) triangles. The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides adjacent to the right angle. The hypotenuse is the side of the triangle opposite the right angle. Hence, using the figure as a guide: a^2+b^2=c^2 If you know any two of the three variables above (a, b, and c), the third can be easily calculated.

Calculating lengths of triangle sides (Pythagorean) - Free Math Help

being given, calculate the third side marked by a tener wo sides being ked by a letter in each right angled triangle. b (ii) - 5 29 211 What is the length

cos) You hove given a trigagle with two slos of equal leght

How to use geometric mean with right triangles

Question Video: Identifying the Possible Lengths of the Third Side of a Triangle Given the Other Sides' Lengths
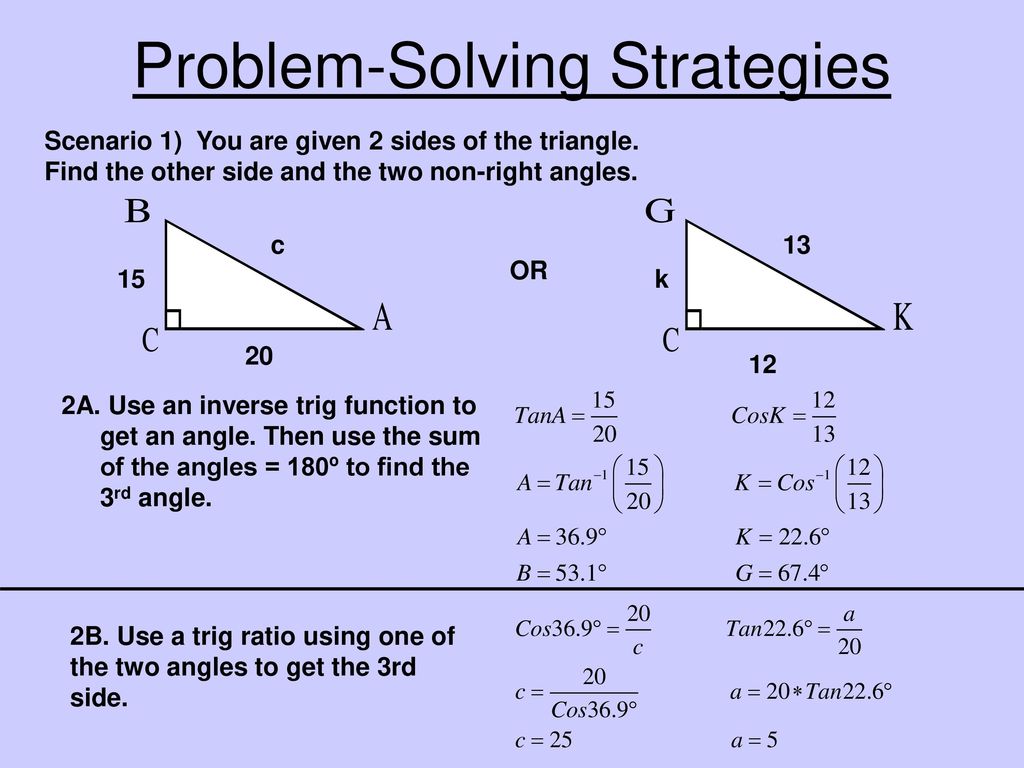
UNIT QUESTION: What patterns can I find in right triangles? - ppt download

Prove that a triangle with sides: (x^2 - 1), 2x, and (x^2 + 1) is
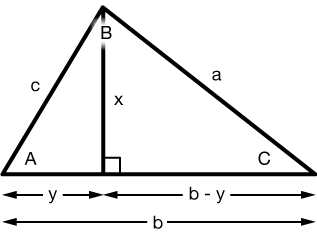
Non-right triangle trig
If two sides of a right-angled triangle are equal, is the third side also equal? - Quora

Non-right Triangles: Law of Cosines

Unit Four - The cRRASZy Minds