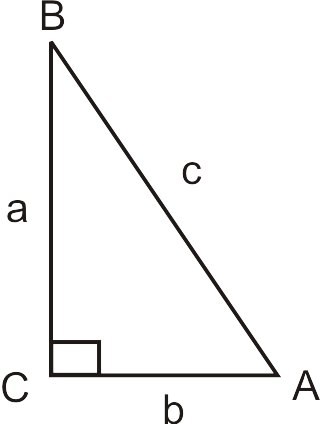
How do you use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the following triangle with sides a, b, & c is a right triangle: a=5, b=10, c=15?
$ 5.99 · 4.6 (682) · In stock
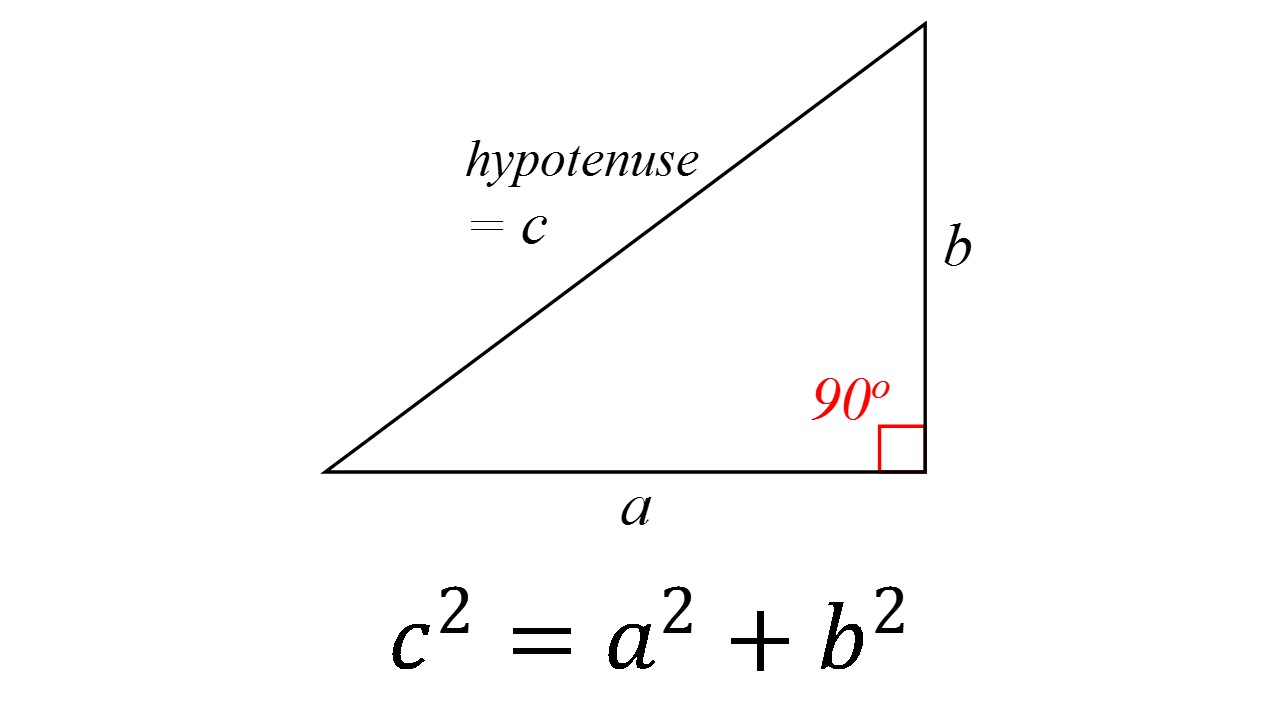
c^2 != a^2 + b^2, therefore, this cannot be a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem applies to right angle triangles, where the sides a and b are those which intersect at right angle. The third side, the hypotenuse, is then c To test whether the given lengths of sides create a right triangle, we need to substitute them into the Pythagorean Theorem - if it works out then it is a right angle triangle: c^2 = a^2 + b^2 15^2 != 5^2+10^2 225 != 25+100 225 != 125 In reality, if a=5 and b=10 then c would have to be c^2 = 125 c =sqrt(125) = 5sqrt(5)~= 11.2 which is smaller than the proposed value in the question. Therefore, this cannot be a right triangle.

Answered: Is the following shape a right…
Pythagorean Theorem - Math Steps, Examples & Questions
Right Triangle Calculator - Find Any Side or Angle - Inch Calculator
What are the measures of the acute angles in a right triangle with
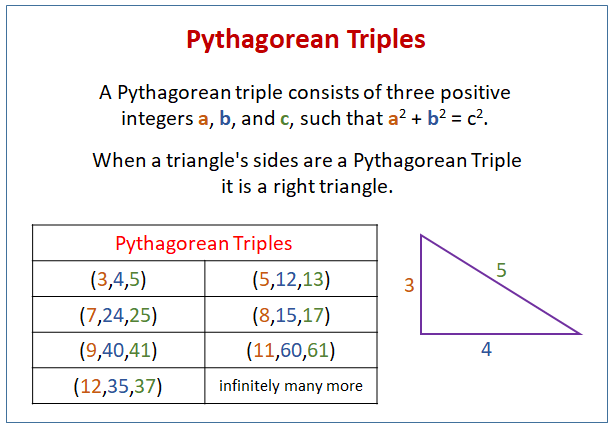
Pythagorean Triples (video lessons, examples, step-by-step solutions)
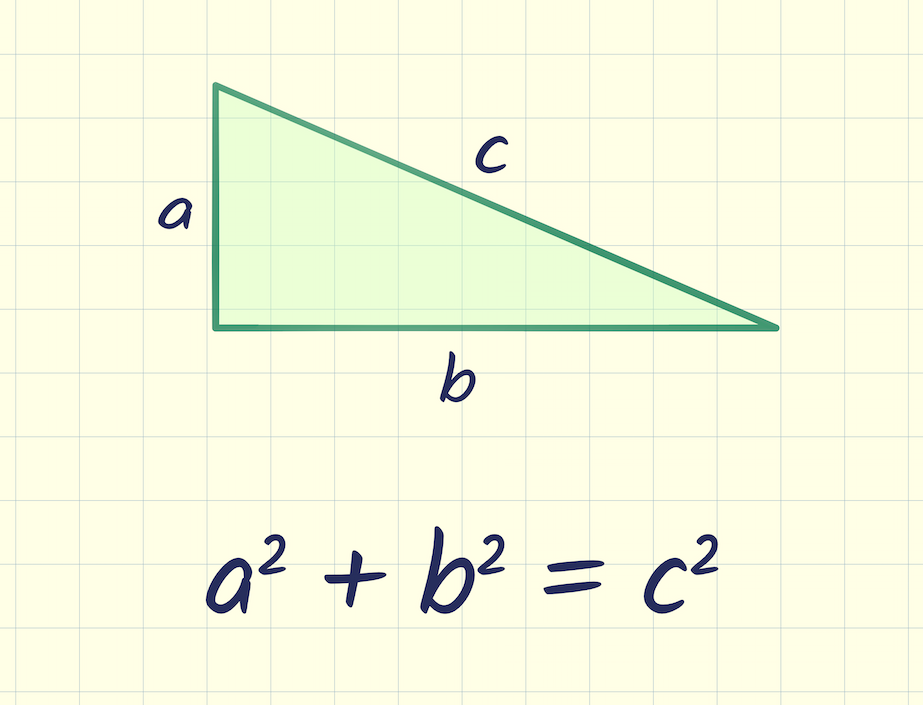
Why the Pythagorean Theorem Is True, by Slawomir Chodnicki

1 9.1 and 9.2 The Pythagorean Theorem. 2 A B C Given any right

Pythagoras Theorem Questions (with Answers) – Math Novice

Pythagorean Theorem Calculator - Quadratic Formula Calculator

How to find the area of a right triangle using the Pythagorean

Non-right Triangles: Law of Cosines
Solved Suppose ABC is a right triangle with sides of lengths
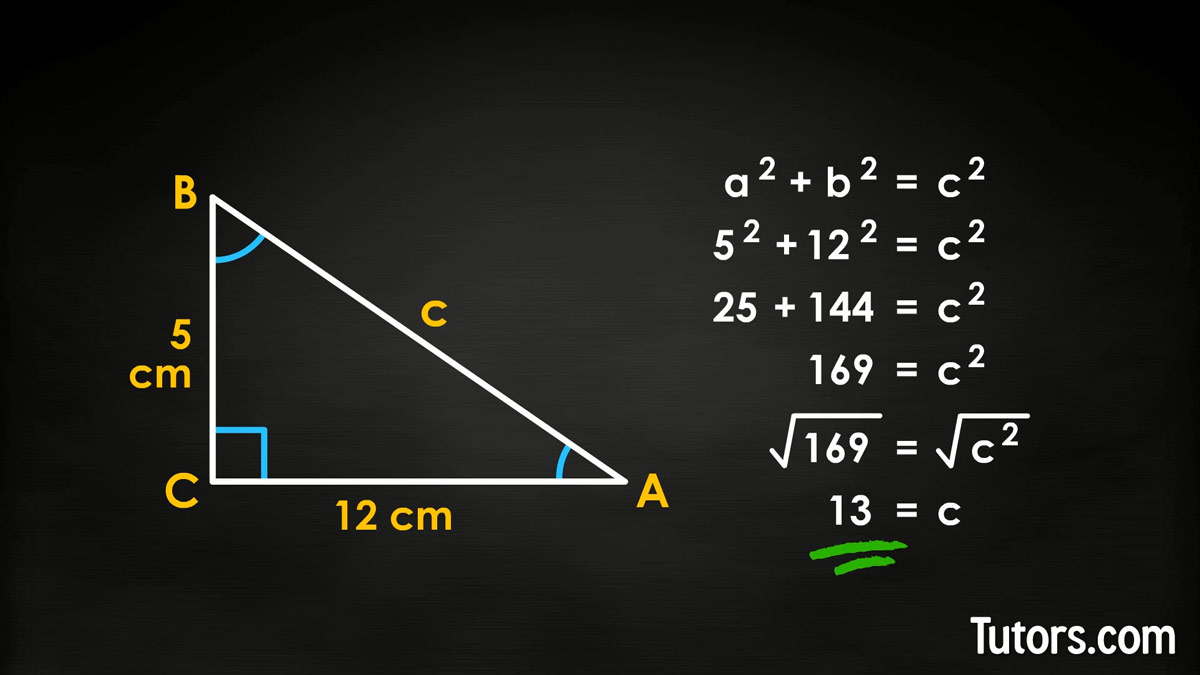
Pythagorean Theorem [Video] Formula, Definition, Examples & Proof
In the right triangle ΔABC, ∠A=90∘ and ∠B=60∘. If BC=10, what
The Pythagorean Theorem