The compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der
$ 5.99 · 4.8 (419) · In stock

For 1 mol of a gas, the van der Waals equation is (P+(a)/(V(m)^(2)))(V(m)-b)=RT Ignoring b, we get (given volume of gas molecule is negligible) (P+(a)/(V(m)^(2)))V(m)=RT ltbgt or pV(m)+(a)/(V(m))=RT or (pV(m))/(RT)+(a)/(V(m)RT)=1 or Z=(pV(m))/(RT)=1-(a)/(V(m)RT) (i) It is given that Z=(pV(m))/(RT)=0.5implies V(m)=(0.5RT)/(P) With this, equation (i) becomes 0.5=1-(a)/((0.5RT//p)RT) or a=(0.5)((0.5RT)/(p))RT=0.25(R^(2)T^(2))/(p) Substiuting the given values, we get a=(0.25)[((0.082L atm K^(-1)mol^(-1))^(2)(273 K)^(2))/((100 atm))] =1.2528 L^(2) atm mol^(-2)

is characterised by van der Waals coefficients that are dependent on t

At 27^(@)C, hydrogen is leaked through a tiny hole into a vessel for 2
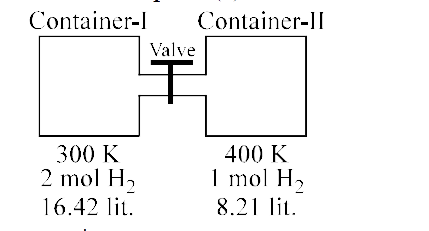
Moles in each compartment are same after opening the valve.

An LPG cylinder weighs 14.8 kg when empty. When full it weighs 29.0 kg
The compressibility factor of gases is less than unity at STP. Therefo
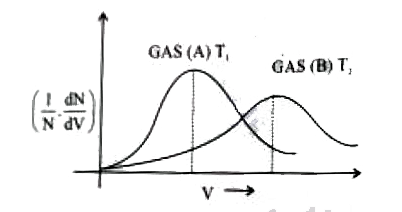
For two gases A and B,P v//s V isotherms are drawn at T K as shown, T
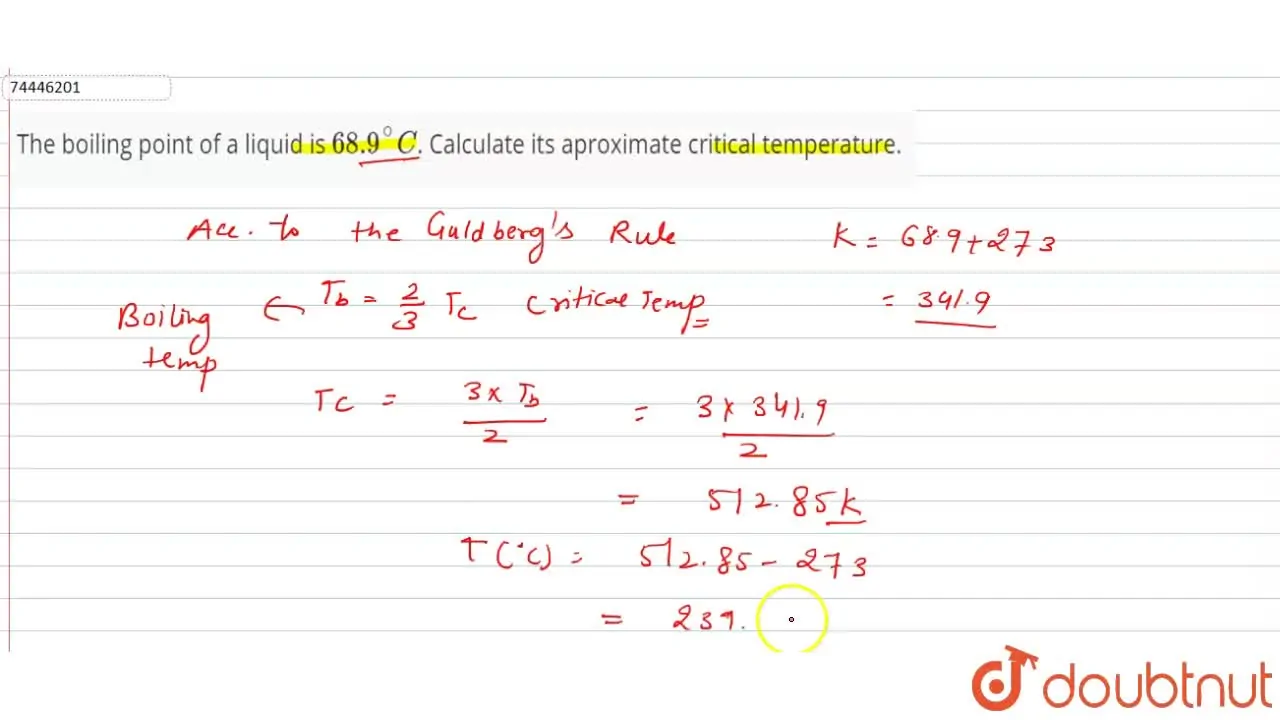
The boiling point of a liquid is 68.9^(@)C. Calculate its aproximate c

The ratio of rate of diffusion of gases A and B is 1:4 and their molar

Only a small number of molecules have very high velocity.
The compression factor (compressibility factor) for one mole of a

Match the entries in column I with entries in Column II and then pick
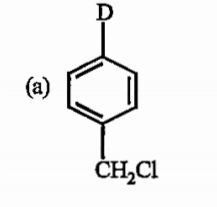
The final product obtained in the reaction
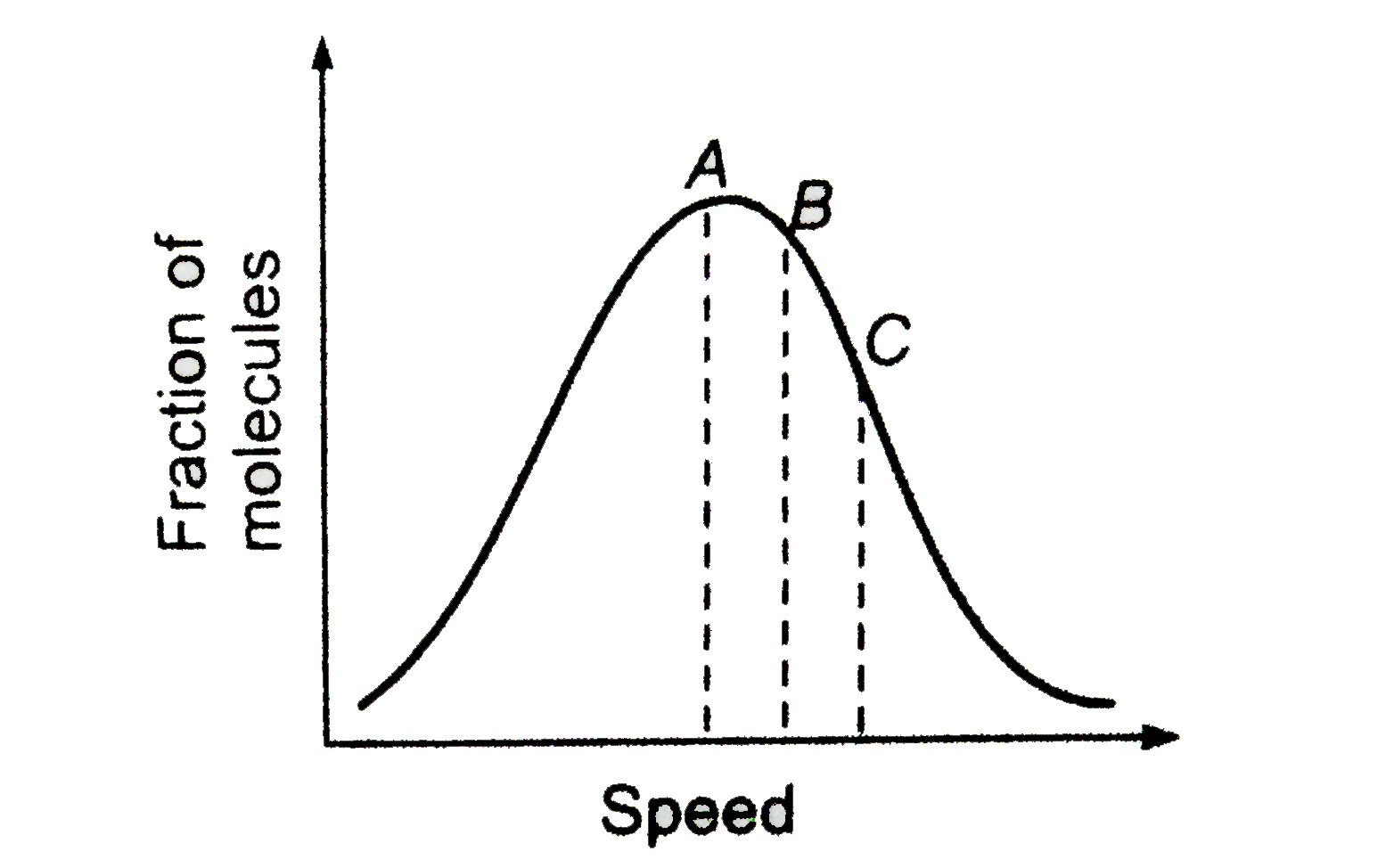
Distribution of molecules with velocity is represented by the curve

A 4:1 molar mixture of He and CH(4) is contained in a vessel at 20 bar