Influence of dopants on the structure and catalytic features of
$ 14.99 · 4.9 (164) · In stock
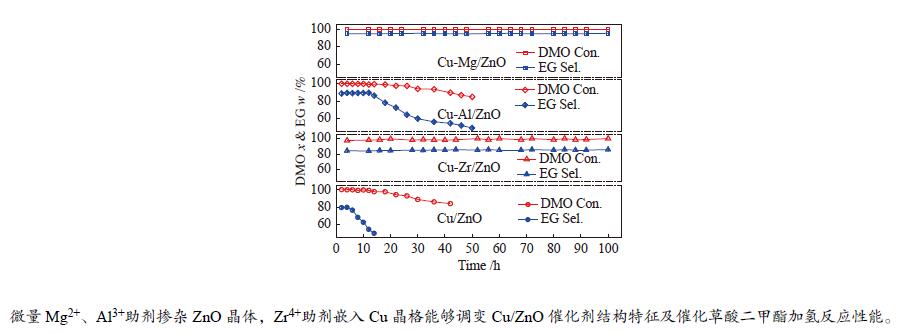
The Cu-<i>M</i>/ZnO catalysts (<i>M</i> = Zr<sup>4+</sup>, Al<sup>3+</sup> and Mg<sup>2+</sup>) for dimethyl oxalate (DMO) selective hydrogenation to ethylene glycol (EG) were synthesized by the co-precipitation method. The properties of the as-synthesized catalysts were characterized by N<sub>2</sub>-physisorption, N<sub>2</sub>O-titration, XRD, H<sub>2</sub>-TPR, CO<sub>2</sub>-TPD, SEM, FT-IR and XPS. It was found that the Cu dispersion could be effectively promoted by the dopants incorporated in the Cu/ZnO catalyst. Particularly, a trace amount of Mg<sup>2+ </sup>and Al<sup>3+</sup> dopants could significantly reinforce the chemical interaction between the Cu and ZnO phases by embedding into the ZnO lattice, while the Cu/ZrO<sub>2 </sub>interaction could be improved with the introduction of Zr<sup>4+</sup>. For DMO gas-phase hydrogenation, the EG yield of the Cu/ZnO catalyst increased from 75.0% to 85.0% and 90.0% in the presence of Zr<sup>4+ </sup>and Al<sup>3+ </sup>dopants, respectively. Particularly, the EG selectivity of Cu-Mg/ZnO catalyst reached up to 95.0% with DMO completely converted for more than 100 h. The correlation between the catalytic behavior and physicochemical features of the Cu/ZnO based catalysts suggested that the surface Cu<sup>+</sup> sites was vital for the catalytic behavior with adequate Cu<sup>0</sup> sites. Additionally, the strengthened Cu/oxide interaction favored the outstanding stability of the Cu-Zr/ZnO and Cu-Mg/ZnO catalyst for DMO hydrogenation.
Catalysts, Free Full-Text

Summary of physical properties affecting carbon-based catalyst and

The relationship between the structure and catalytic performance Cu/ZnO/ZrO2 catalysts for hydrogenation of dimethyl 1,4-cyclohexane dicarboxylate - ScienceDirect

Promoting Strong Metal Support Interaction: Doping ZnO for Enhanced Activity of Cu/ZnO:M (M = Al, Ga, Mg) Catalysts
Catalysts, Free Full-Text
Electrochemical reactions catalyzed by carbon dots from

Effect of leaching temperature on structure and performance of Raney Cu catalysts for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate

Influence of dopant substitution mechanism on catalytic properties
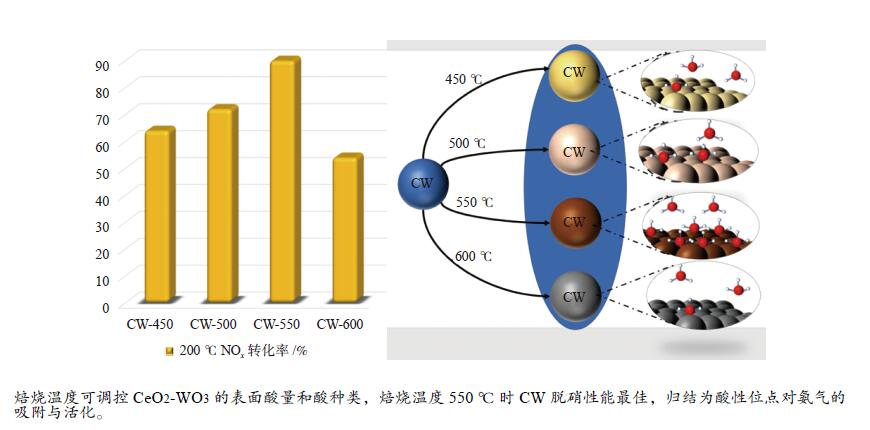
燃料化学学报(中英文)

Catalyst activation: Surface doping effects of group VI transition

Effect of leaching temperature on structure and performance of Raney Cu catalysts for hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate - ScienceDirect

Hydrogenolysis of glycerol over homogenously dispersed copper on solid base catalysts

Recent trends on density functional theory–assisted calculations

Promoting Strong Metal Support Interaction: Doping ZnO for Enhanced Activity of Cu/ZnO:M (M = Al, Ga, Mg) Catalysts